How To Find Resultant Velocity After Collision
Elastic collision is used to find the final velocities v1. How Do I Calculate Resultant Velocity.
What Are Velocity Components Article Khan Academy
Active 5 years 6 months ago.

How to find resultant velocity after collision. A component normal to the wall v_perp and a component parallel to the wall v_parallel. Homework Equations mv m1v1 m2v2 m1v1 m2v2 Speed Square root of X-velocity2 Y-velocity2 The Attempt at a Solution. The x component of a vector is parallel to the.
50000 views later on a video made for a Canadian student via youtube request. M 1 v 1 m 1 m 2v 2 Where m 1m 2 - Mass of Objects v 1v 2 - Velocity of Objects. Calculating the resultant velocity vector after a 2D collision.
In case the ball doesnt rotate we have v_parallelv_parallel where the prime indicates the. The complaint Ive had over time is. After the hit the players tangle up and move with the same final velocity.
Ask Question Asked 5 years 6 months ago. Hence momentum conservation in the. It is an easy straightforward problem to find the velocity of the center of mass of the two-car system immediately after the collision.
P m v but we can rearrange this equation so that v p m. The final velocity can be found for the combined paintball and can by rearranging the formula. M1 m2 vf m1v.
Ie times the -component of the first objects final velocity. Likewise the final -momentum of the second object is. In elastic collision of ball to wall along x axis mVixmVfx as velocity of wall is 0 before and after collision thus VixVfx eq1 Kinetic Energy is conserved so mVi2 mVf2 Vix2.
The mass of the paintball is 0200 g which is equal to 0000200 kg and the mass of the can is 150 g which is equal to 0015 kg. If you run your bumper car into a friends bumper car along a straight line you bounce off and kinetic energy. Velocity after the collision 60000 20000 3 ms.
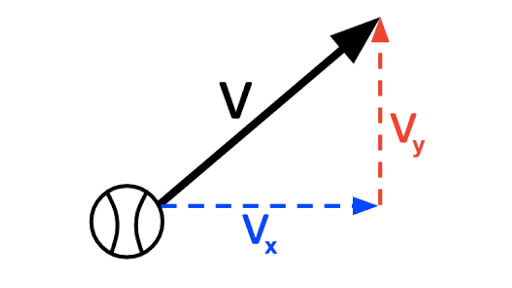
Knowing the x- eastward and y- northward components of the velocity of the center of mass the magnitude is. The initial velocity of the paintball is 900 ms. Calculate the x and y.
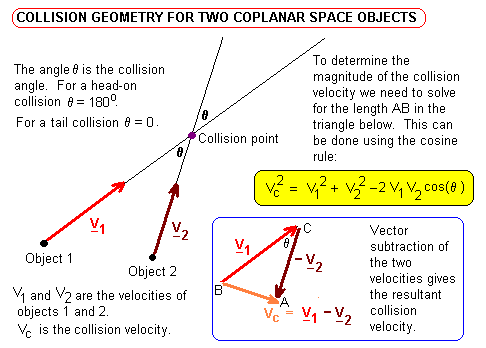
Currently I have a mini physics game which uses Separating Axis Theorem for collision detecting and response however I came to a standstill when I discovered that there wasnt much. Find the magnitude and angle for each velocity given. The following formula is used to calculate the velocities of two objects after an elastic collision.
M1vi1 m2vi2 m1vf1 m2vf2 vf1 m1 m2vI1 2 m2vI2 m1 m2 vf2 2 m1vI1 m1 m2vI2 m1 m2. First you want to find the angle between each initial velocity. How do I calculate the resultant velocities assuming no elasticity or friction.
After the collision the -momentum of the first object is. M1v1 m2v2cos theta m1 m2 v3 cos phi This is for the x axis m1v1 m2v2sin theta m1 m2 v3 sin phi This is for the y axis In these equations v3 is the final velocity of the resultant mass and phi is the resultant angle of travel. With what velocity will the two cars be moving immediately after the collision.
Also the angle that the velocity vector makes with the x-. In physics the most basic way to look at elastic collisions is to examine how the collisions work along a straight line. Solving when final velocities are unknown.
First the x- and y-components of the velocity of the center of mass. V 1 m 1 - m 2 m 1 m 2 v 1 v 2 2m 1 m 1 m 2 v 1 Where m 1 m 2 - Mass of Moving Objects v 1 - Velocity of Moving Objects. Viewed 486 times 3 1.
Therefore the final momentum pf must equal the combined mass of the two players multiplied by their final velocity m1 m2 vf which gives you the following equation. First step is to decompose the velocity at the time of collision into two components. The two collide not necessarily head-on one could broadside the other etc.
The speed of the bullet just before it hit the block was about 150 ms. Before the collision the total -momentum is zero since there is initially no motion along the -axis. For the mass of moving objects m1 and m2.
0 m2v2 m1 m2vy vy m2v2 m1 m2 vy 666 kmh v vx vy v 1295 kmh. Therefore the velocity of the center of mass of the system is 12 ms the velocity of the bullet block after the collision. M1v1 0 m1 m2vx vx m1v1 m1 m2 vx 1111 kmh y-direction.
Calculate the x and y components of the individual velocity vectors. When a collision between two objects is elastic kinetic energy is conserved. Watch this illustrated podcast on momentum for a summary of how.
If v 1 the velocity of the bullet and v 2 the initial velocity of the block 0 ms then.

A Cartoon Guide To Physics Momentum Angry Bird Special Part 2 Physics Poster Momentum Physics Introduction To Physics

Inelastic Collisions In One Dimension Physics

The Exploding Carts Interactive Animates Several Explosions Between Two Carts On A No Friction Track The Explosions Physics Momentum Physics Physics Concepts

Momentum Calculations Problem Solving Using Law Of Conservation Of Momentum Newton S Third Law Elastic Inelastic Collisions Kinetic Energy Practice Questions Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes

9 5 Collisions In Multiple Dimensions University Physics Volume 1

Calculating Relative Velocity Video Khan Academy

Addition Of Velocities Physics

Unit 2 Momentum Conservation Name Date Period Worksheet Conservation Of Momentum Chapter 8 Momentum Directions Answer The Following Questions Course Hero

Relative Velocity Colliding Particles Example 2010hl Youtube

Pin By Vanessa Owen On Fizik Dan Sains Gcse Physics Physics Lessons Physics

Collisions Of Point Masses In Two Dimensions Physics

Notes Mind Map In 2021 Physics Notes Physics Lessons Physics Teaching Ideas

Resultant Motion Physics For K 12 Openstax Cnx
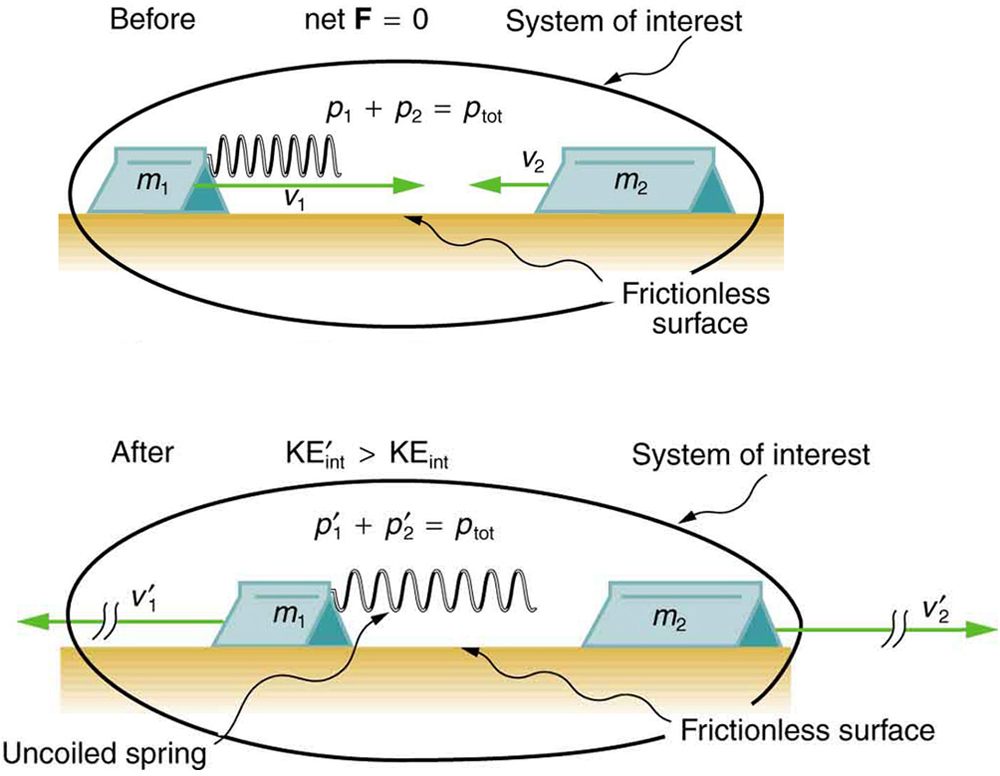
Inelastic Collisions In One Dimension College Physics

Net Force Ranking Tasks Concept Builder Provides Learners An Opportunity To Use The Concept Of Net Force And Newton S Seco Physics Projects Body Diagram Force


Post a Comment for "How To Find Resultant Velocity After Collision"